User Guide

LingoGO! is a desktop app for university students who use English as their first language and are trying to learn a new language. Founded on the widely established learning technique of spaced-repetition, LingoGO! takes all the benefits of pen-and-paper flashcards in learning, and brings them to the next level with our powerful indexing and sharing features – without the hassle of managing actual physical ones. Coupled with our unique Command Line Interface (CLI) and an elegant Graphical User Interface (GUI) to accompany it, LingoGO! is sure to delight you, and empower you on your journey in mastering the new language you have always wanted.
LingoGO! currently supports all languages that can be represented on your computer and has the following main features:
- Addition, deletion, and editing of flashcards.
- Finding and filtering of flashcards by keywords and conditions.
- Importing and exporting of flashcards to be shared with others.
- Testing your knowledge in a questionnaire of flashcards.
Detailed information about these features can be found under the Modes and Commands sections in this user guide.
Table of Contents
- Purpose of the user guide
- How to use the user guide
- Quick start
- Modes
-
Commands
- Adding a flashcard:
add - Answering a flashcard :
answer - Clearing all flashcards :
clear - Deleting a flashcard :
delete - Editing a flashcard :
edit - Exiting LingoGO! :
exit - Exporting flashcards :
export - Filtering flashcards by condition(s):
filter - Locating flashcards by keyword(s):
find - Viewing help :
help - Importing flashcards :
import - Listing all flashcards :
list [NUMBER_OF_FLASHCARDS] - Moving to the next flashcard in slideshow mode :
next - Moving to the previous flashcard in slideshow mode :
previous - Testing with a set of flashcards :
slideshow - Exiting slideshow mode:
stop
- Adding a flashcard:
- Data
- Glossary
- FAQ
- Command summary
Purpose of the user guide
This user guide aims to help users familiarise themselves with the commands of LingoGO! and use the application effectively.
How to use the user guide
- A Table of Contents with clickable links can be found above to help with navigating across the user guide quickly.
- New users can refer to the Quick Start guide for a quick set-up tutorial.
- New users can also refer to Modes to start understanding how to use LingoGO!.
- A detailed outline of the commands can be found under Commands.
- Experienced users can refer to the Command Summary for a quick overview of all the commands in LingoGo!.
- A Glossary is provided to help explain certain important terms used in this guide.
Quick start
-
Ensure you have Java 11 or above installed in your Computer (you may download Java from here).
-
Download the latest lingogo.jar from here.
-
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for LingoGO!.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The following GUI should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
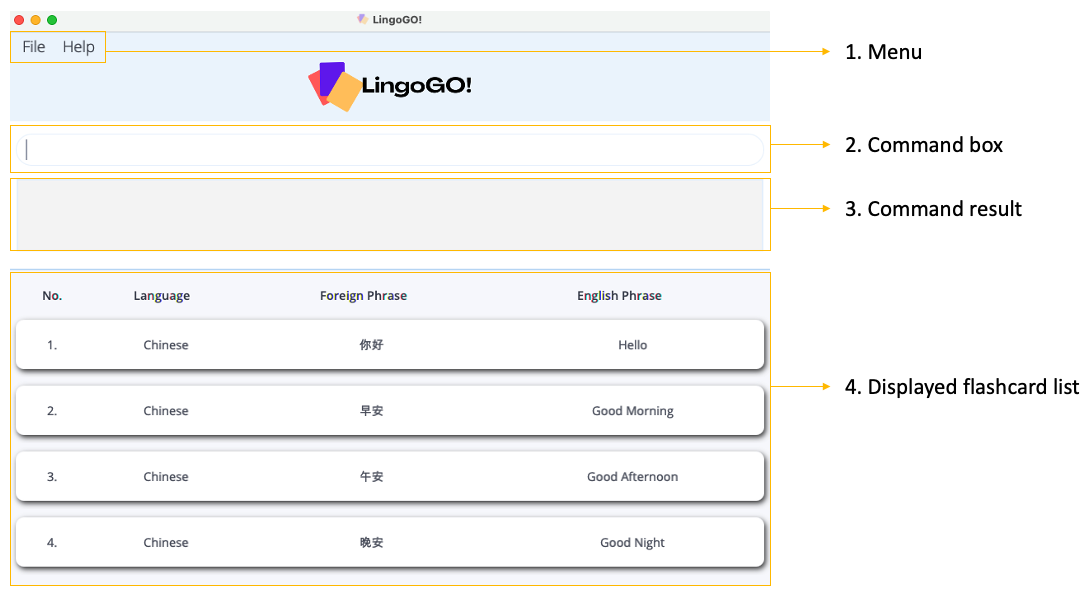
Below is an overview of the GUI, with the corresponding number label:
-
Menu
- A clickable menu bar.
-
Command box
- Type a command into the command box and press Enter to execute it.
- Some example commands you can try (refer to the Commands section below for a full list of commands and their details):
-
list: Lists all flashcards. -
add l/Chinese e/Good Morning f/早安: Adds a flashcard with theChineselanguage, English phraseGood Morning, and corresponding foreign phrase早安. -
delete 3: Deletes the 3rd flashcard shown in the current displayed list. -
find e/Good Morning: Finds flashcard(s) with the matching English phraseGood Morning. -
filter l/Chinese: Shows only the flashcard(s) with theChineselanguage in the current displayed list.
-
Command result
- Shows a message after you execute a command.
-
Displayed flashcard list
- Shows a list of your flashcards.
-
Menu
Modes
Before diving into the specific commands, let’s have an overview of the different modes in LingoGO!.
LingoGO! has two main modes, List mode and Slideshow mode, through which users can interact with the application. At a high level, List mode provides an intuitive table overview to manage flashcards with our powerful and flexible indexing features. In contrast, Slideshow mode allows users to test their knowledge on selected flashcards one by one in a questionnaire-style interface while retaining the feel and look of traditional flashcards.
The following two sections will describe these modes in further detail.
List mode
Below is an example of what LingoGO! looks like in list mode.
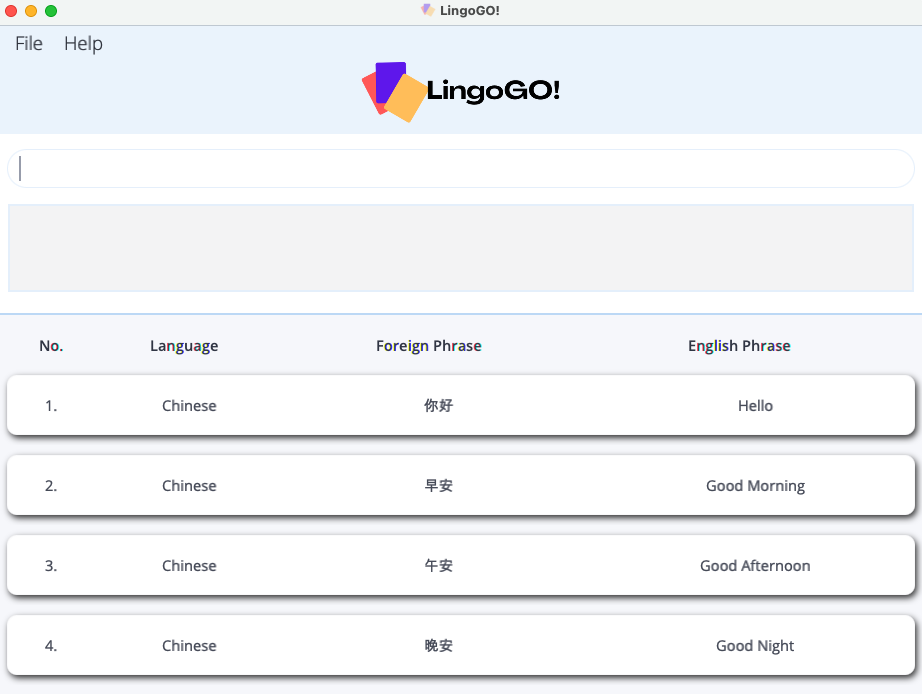
LingoGO! always starts in list mode and displays all of your flashcards.
List mode lets you add, delete,
edit, import, and export
flashcards.
List mode also lets you choose what flashcards to display. The displayed flashcards
will be the flashcards you get tested on when you switch to slideshow mode.
You can use the list, filter, or
find command to choose which flashcards to display.
Slideshow mode
Below is an example of what LingoGO! looks like in slideshow mode.
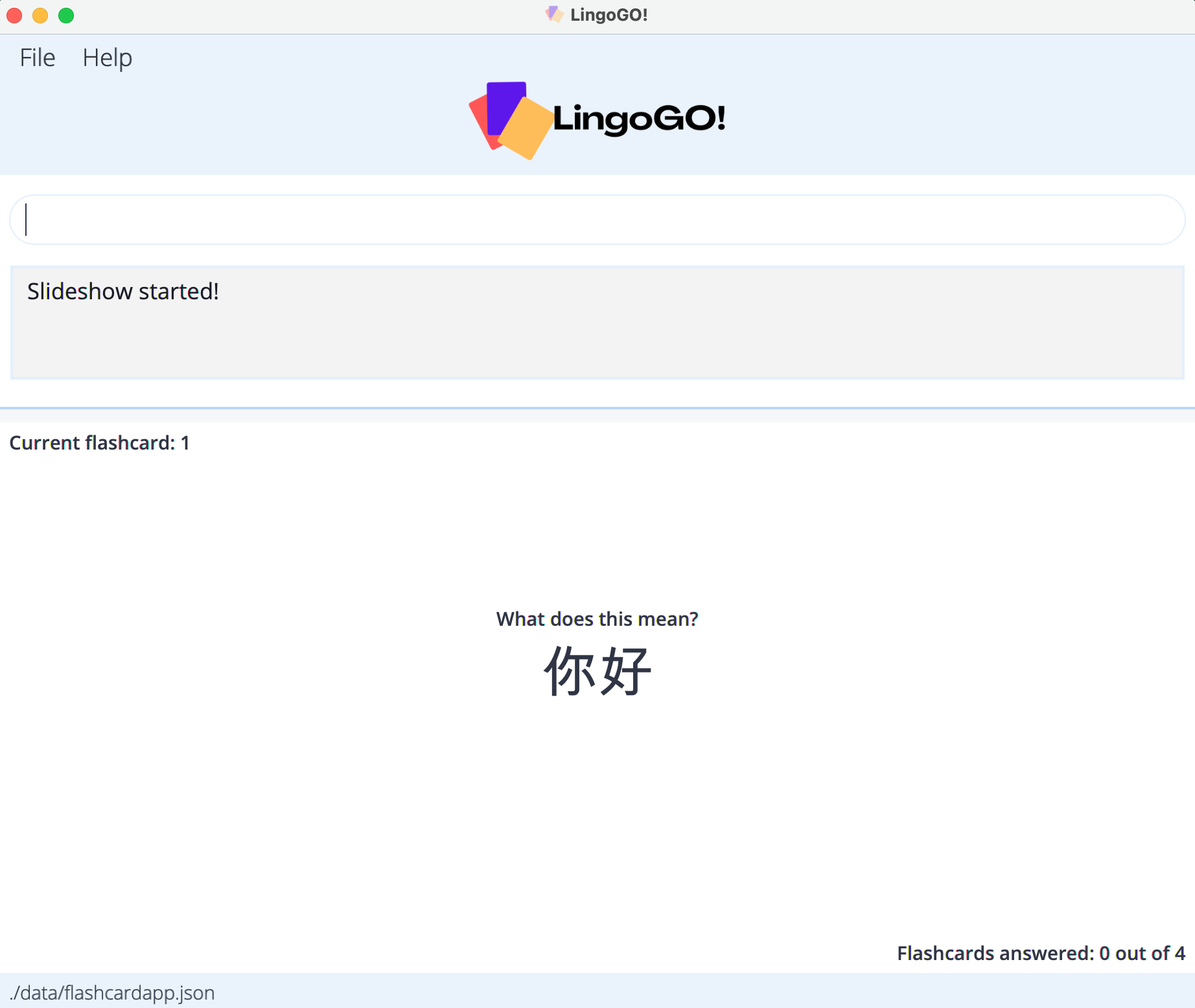
Slideshow mode tests your knowledge by showing you flashcards one at a time. The flashcards shown to you are the ones displayed in list mode.
To enter and exit slideshow mode, use the slideshow and stop commands respectively.
In slideshow mode, you can:
![]() Notes about slideshow mode:
Notes about slideshow mode:
- If your flashcards have phrases that are too long to be displayed, you can increase the app’s window size.
Commands
The following section gives an indepth overview of each command in the application, and provides some examples on their usages.
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
- Words in
UPPER_CASEare parameters to be supplied by you.- e.g. a usage of
add l/LANGUAGE e/ENGLISH_PHRASE f/FOREIGN_PHRASEcould beadd l/Chinese e/Good Morning f/早安.
- e.g. a usage of
- Items in square brackets are optional.
- e.g.
edit INDEX [l/LANGUAGE] [e/ENGLISH_PHRASE] [f/FOREIGN_PHRASE]can be used asedit 1 l/Chinese e/Good Morning f/早安oredit 1 e/Good Morning.
- e.g.
- Parameters can be in any order.
- e.g. if the command specifies
add l/LANGUAGE e/ENGLISH_PHRASE f/FOREIGN_PHRASE,add f/FOREIGN_PHRASE l/LANGUAGE e/ENGLISH_PHRASEis also acceptable.
- e.g. if the command specifies
- If a parameter is expected only once, but you specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence will be taken.
- e.g.
edit 2 e/Hi e/Hellois the same asedit 2 e/Hello.
- e.g.
- Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
helpandclear) will be ignored.- e.g.
help 123is the same ashelp.
- e.g.
Adding a flashcard: add
Adds a flashcard to LingoGO!.
- The flashcard will be added to the bottom of the displayed flashcard list in list mode.
Format: add l/LANGUAGE e/ENGLISH_PHRASE f/FOREIGN_PHRASE
![]() Notes about adding flashcards:
Notes about adding flashcards:
-
ENGLISH_PHRASEandFOREIGN_PHRASEshould not be longer than 100 characters. For optimal viewing experience, flashcard phrases should be kept as short as possible. If your phrases are too long to be displayed, you can increase the app’s window size.
Examples:
add l/Chinese e/Good Morning f/早安
Answering a flashcard : answer
Checks whether the English phrase of a flashcard matches the phrase you provide.
Format: answer e/ENGLISH_PHRASE
- Checks the English phrase of the displayed flashcard against the
ENGLISH_PHRASEyou provide. - The app will then show the correct English phrase and tell you whether you got it right.
-
ENGLISH_PHRASEis not case-sensitive (e.g. “HeLLo” matches “hello”). - You can only answer a flashcard in slideshow mode, and you can only answer it once.
Examples:
-
answer e/hellochecks the English phrase of the flashcard on display to see ifhellomatches it.
Clearing all flashcards : clear
Clears all flashcards from LingoGO!.
Format: clear
Deleting a flashcard : delete
Deletes the specified flashcard from LingoGO!.
Format: delete INDEX
- Deletes the flashcard at the specified
INDEX. -
INDEXrefers to the index number of the flashcard shown in list mode. -
INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
-
listfollowed bydelete 2deletes the 2nd flashcard in LingoGO!. -
find Hellofollowed bydelete 1deletes the 1st flashcard from the results of thefindcommand.
Editing a flashcard : edit
Edits an existing flashcard in LingoGO!.
Format: edit INDEX [l/LANGUAGE] [e/ENGLISH_PHRASE] [f/FOREIGN_PHRASE]
- Edits the flashcard at the specified
INDEX. -
INDEXrefers to the index number of the flashcard shown in list mode. -
INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
![]() Notes about editing flashcards:
Notes about editing flashcards:
-
ENGLISH_PHRASEandFOREIGN_PHRASEshould not be longer than 100 characters. For optimal viewing experience, flashcard phrases should be kept as short as possible. If your phrases are too long to be displayed, you can increase the app’s window size.
Examples:
-
edit 1 l/GermanEdits the language of the 1st flashcard to beGerman. -
edit 1 e/Good MorningEdits the English phrase of the 1st flashcard to beGood Morning. -
edit 2 f/Guten MorgenEdits the foreign phrase of the 2nd flashcard to beGuten Morgen. -
edit 2 l/German e/Good Morning f/Guten MorgenEdits the language, English phrase, and foreign phrase of the 2nd flashcard to beGerman,Good Morning, andGuten Morgenrespectively.
Exiting LingoGO! : exit
Exits the app.
Format: exit
Exporting flashcards : export
Exports the currently displayed flashcards in list mode to a CSV file.
![]() Notes about opening CSV files with Excel:
Notes about opening CSV files with Excel:
- We advise changing the default settings so that foreign language is properly displayed with Excel. Please refer here for detailed instructions.
Format: export CSV_FILE_NAME
- Provides a file name with a .csv extension in which the flashcards will be stored and exported.
- The exported file will be added to the data folder (located in the same folder as the lingogo.jar file).
- The CSV file will have 3 columns in this order from left to right:
- Language
- Foreign phrase
- English phrase
Examples:
-
export myCards.csvwill save all cards in LingoGO! to a CSV file namedmyCards.csv.
Filtering flashcards by condition(s): filter
Filters flashcards based on the specified condition(s).
Format: filter [l/LANGUAGE] [i/INDEX_LIST] [r/INDEX_RANGE]
-
LANGUAGEis not case-sensitive (e.g. “Chinese” matches “CHINESE”). -
INDEX_LISTis a list of space separated indices, that refer to the indices shown in the current displayed list. -
INDEX_RANGEis a pair of space separated indices, that refer to the indices shown in the current displayed list. The given range is inclusive, that is1 3would refer to the flashcards at indices 1, 2 and 3. Also the first given index must be smaller or equal to the second given index. e.g.1 2,3 14are accepted but not1 2 3nor3 1. - The indices must be positive integers 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
-
filter l/Chinesereturns all flashcards with theChineselanguage likee/Good Morning f/早安. -
filter i/1 2 3returns the flashcards in list mode indexed at 1, 2 and 3. -
filter r/2 4returns all the flashcards in list mode indexed from 2 to 4. -
filter i/1 3 6 l/Tamilreturns all the flashcards in list mode indexed at 1, 3 and 6 with theTamillanguage. -
filter l/Chinese r/1 4returns all the flashcards in list mode indexed from 1 to 4 with theChineselanguage.
Locating flashcards by keyword(s): find
Finds flashcards based on the keyword(s) specified.
Format: find [e/ENGLISH_KEYWORDS] [f/FOREIGN_KEYWORDS]
- The search is not case-sensitive, e.g
HELLOwill matchHello. - The order of the keywords does not matter, e.g.
Good morningwill matchMorning good. - Only full words will be matched for English keywords, e.g.
Hellowill not matchHelloooo. -
Non-full words match will be accepted for foreign keywords, e.g.
早with match早安. - Flashcard(s) matching at least one keyword will be displayed.
- At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
Examples:
-
find e/HELLOreturnse/Hello f/你好 -
find f/早returnse/Good Morning f/早安ande/Morning f/早晨 -
find e/Hello f/早returnse/Hello f/你好,e/Good Morning f/早安ande/Morning f/早晨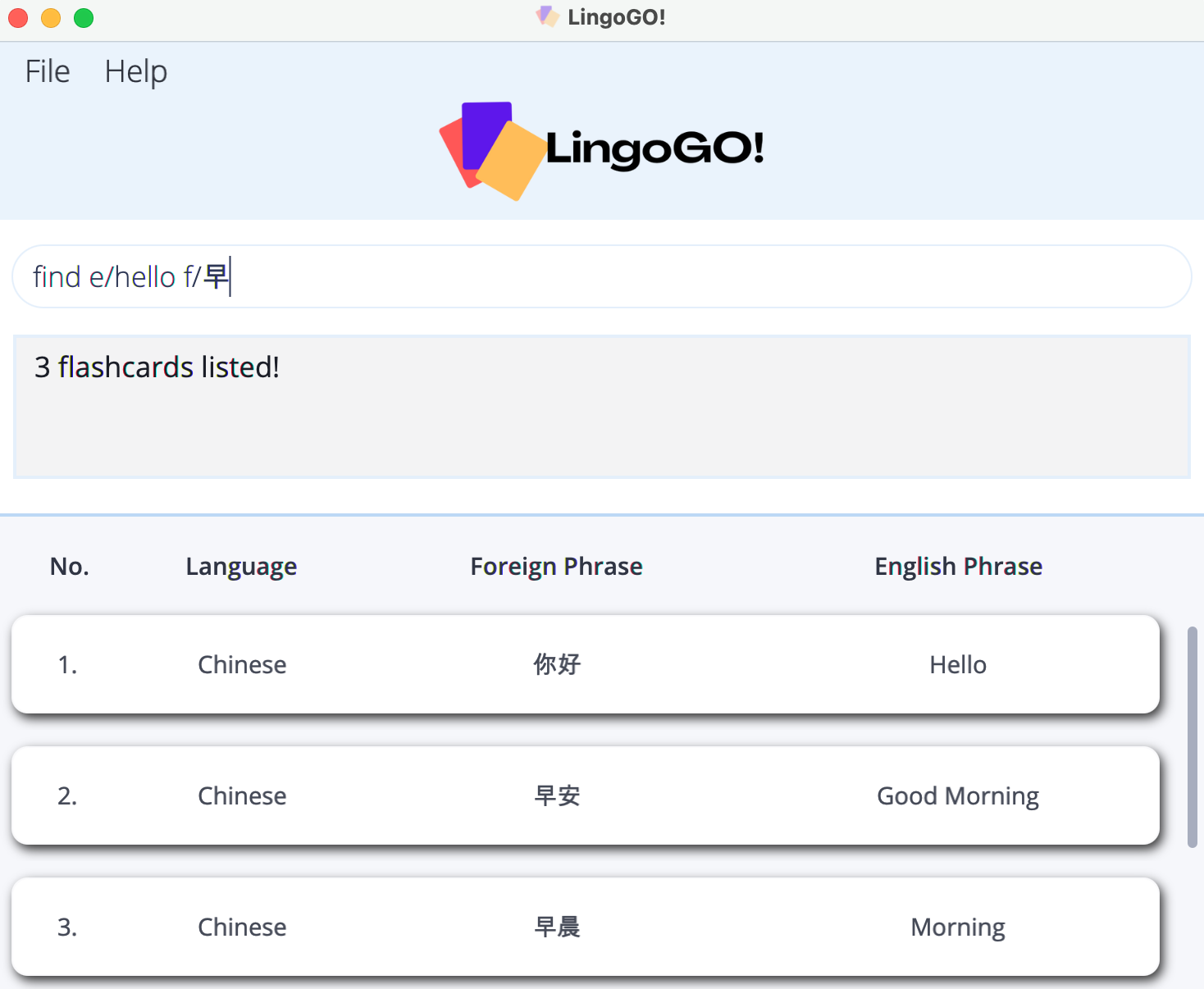
Viewing help : help
Shows a message explaining how to access the help page, as well as dropdowns with brief explanations for each command.
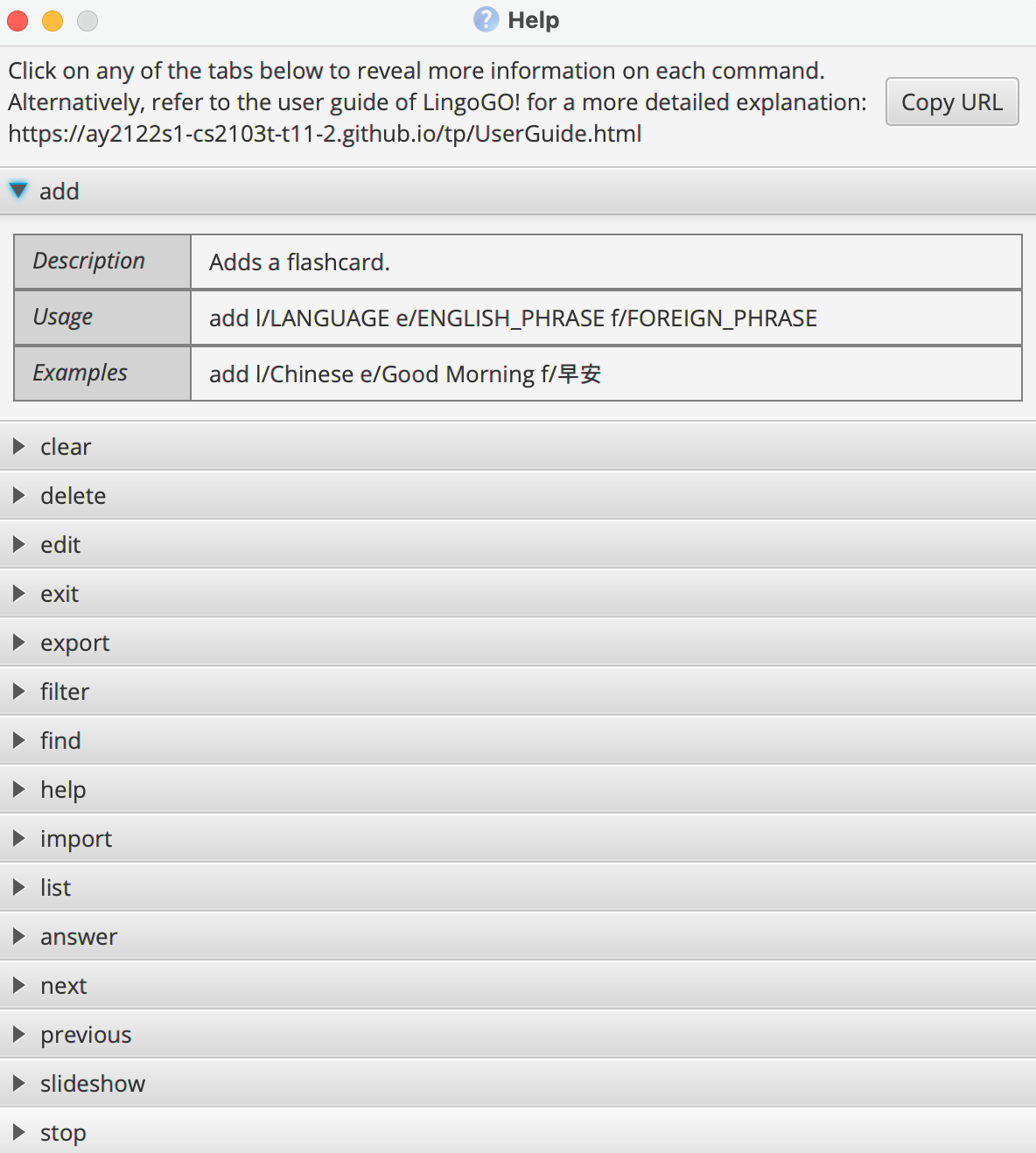
Format: help
Importing flashcards : import
![]() Notes about importing CSV files made with Excel:
Notes about importing CSV files made with Excel:
- We advise against using Excel to create a CSV file to be imported into LingoGO!.
Imports flashcards from a CSV file and adds them to the existing list in LingoGO! (instead of replacing the current list)
Format: import CSV_FILE_NAME
- Place the CSV file that you wish to import in the data folder (located in the same folder as the lingogo.jar file).
- The CSV file must have exact headers “Language, Foreign, English”. (as shown in the below example)
- The CSV file must have 3 columns in this order from left to right:
- Language
- Foreign phrase
- English phrase
![]() Importing invalid CSV file:
Importing invalid CSV file:
- If any of the above required information in the CSV file is invalid or missing, LingoGO! will not import the flashcards
Below is an example of how the CSV file might look like.
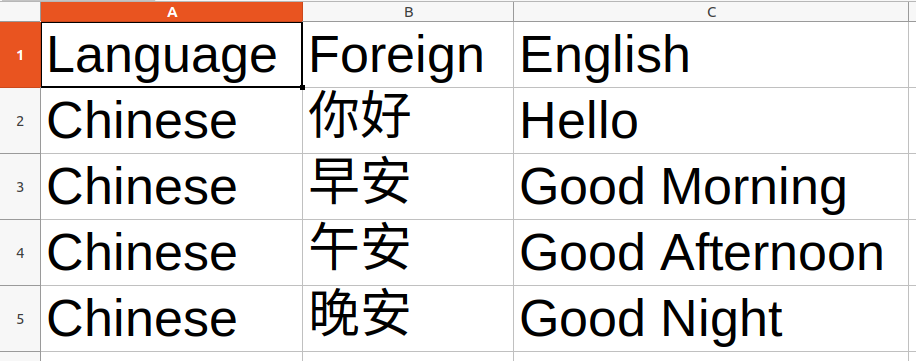
Examples:
-
import dictionary.csvwill add all flashcards stored in the CSV file dictionary.csv to LingoGO!.
Listing all flashcards : list [NUMBER_OF_FLASHCARDS]
Shows a list of flashcards in LingoGO!.
Format: list [NUMBER_OF_FLASHCARDS]
- Lists all flashcards in LingoGO! if
[NUMBER_OF_FLASHCARDS]is not provided - Randomly select
[NUMBER_OF_FLASHCARDS]flashcards to be shown in the list mode - The
[NUMBER_OF_FLASHCARDS]must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
-
listreturns all flashcards in LingoGO!. -
list 3returns 3 randomly selected flashcards in LingoGO!
Moving to the next flashcard in slideshow mode : next
Goes forward to the next flashcard (if there is one) in slideshow mode.
Format: next
Moving to the previous flashcard in slideshow mode : previous
Goes back to the previous flashcard (if there is one) in slideshow mode.
Format: previous
Testing with a set of flashcards : slideshow
Switches to slideshow mode for you to test yourself using the flashcards shown in list mode.
Format: slideshow
Exiting slideshow mode: stop
Exits slideshow mode and returns to list mode.
Format: stop
Data
Saving the data
LingoGO!’s data is saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes its data. There is no need to save manually.
Editing the data file
LingoGO!’s data is saved as a JSON file at {JAR file location}/data/lingogo.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
Glossary
CSV
A CSV file, short for comma-separated values, is a special text file that uses commas for formatting.
File paths
File paths specify the location of a file on the computer, telling the computer how to find a specific file. An absolute file path tells the computer how to find the file from the root folder. A relative file path tells the computer how to find a file from the current folder that it is in. For more on file paths, you may want to visit here.
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous LingoGO! home folder.
Command summary
| Action | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Add | add l/LANGUAGE e/ENGLISH_PHRASE f/FOREIGN_PHRASE |
add l/Chinese e/Good Morning f/早安 |
| Answer | answer e/ENGLISH_PHRASE |
answer e/hello |
| Clear | clear |
clear |
| Delete | delete INDEX |
delete 3 |
| Edit | edit INDEX [l/LANGUAGE] [e/ENGLISH_PHRASE] [f/FOREIGN_PHRASE] |
edit 2 f/Guten Morgen |
| Exit | exit |
exit |
| Export | export FILE_NAME |
export myCards.csv |
| Filter | filter [l/LANGUAGE] [i/INDEX_LIST] [r/INDEX_RANGE] |
filter l/Chinese r/1 4 i/1 2 3 |
| Find | find [e/ENGLISH_KEYWORDS] [f/FOREIGN_KEYWORDS] |
find e/Hello f/早 |
| Help | help |
help |
| Import | import CSV_FILE_PATH |
import dictionary.csv |
| List | list [NUMBER_OF_FLASHCARDS] |
list 4 |
| Next | next |
next |
| Previous | previous |
previous |
| Slideshow | slideshow |
slideshow |
| Stop | stop |
stop |